
What is egg yolk?
Egg yolks are the yellow part at the center of an egg. They contain high levels of cholesterol but also provide a range of vital nutrients and health benefits. Calories in egg yolk may vary depending on the size of the egg.
Eggs are a low cost, nutrient dense food that is easy to access and prepare, making them an excellent dietary staple for many people worldwide.
They are extremely versatile. People can prepare eggs in several different ways or use them in many aspects of food preparation, cooking, and baking.
In this article, we explain the benefits and nutritional breakdown of egg yolks. We also compare them with egg whites and provide tips on how to eat them safely.
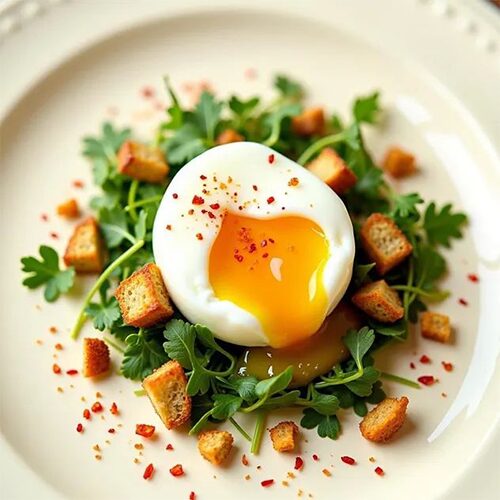
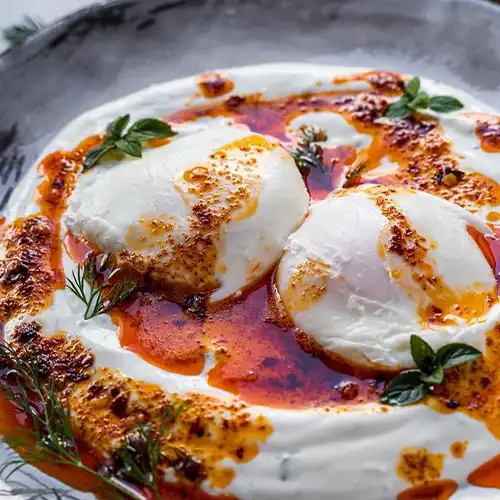


Benefits
Eating the egg white and yolk together in a whole egg provides the right balance of protein, fat, and calories. This combination allows most people to feel fuller and more satisfied after eating eggs in meals.
However, a 2019 reviewTrusted Source suggests that most of the nutrients in an egg are in the yolk. The distribution of the proteins, however, is even throughout the whole egg.
The review highlights several benefits that the nutrients and proteins in egg yolk may provide, including:
- A lower risk of gastrointestinal distress: This benefit may be due to egg yolk proteins, such as phosvitin, which may reduce the number of compounds in the body that cause inflammation.
- A boosted immune system: Certain compounds called sulfated glycopeptides are present in the membrane of the egg yolk. These may stimulate the production of macrophages, which are cells in the immune system that protect the body against disease and infection.
- Lower blood pressure: The review notes that egg yolk contains several compounds called peptides that research has shown to reduce blood pressure significantly in rats. High blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- Reduced risk of vision problems: The American Heart Association state that yolks are a significant sourceTrusted Source of lutein and zeaxanthin. These carotenoids may protect against cataracts and macular degeneration, two common eye problems that often develop after the age of 55 years.
It is worth noting that many of the studies in this review did not test the effects of egg yolks in humans. Instead, they performed the tests in a laboratory or on animals. Therefore, the findings may not apply to humans.
Researchers have also started exploring the potential of various immunostimulants called immunoglobulins, which are present in egg yolks.
For example, a 2017 study found that female mice were less likely to become infected with Helicobacter pylori — bacteria that commonly cause intestinal infection — after consuming anti-VacA IgY, an immunoglobulin in egg yolk.
Nutrition
The nutritional content of an egg yolk depends on the size, origin, and processing of the egg, as well as the species from which it comes.
The final dietary value of egg yolks varies greatly depending on their preparation. For example, cooking whole eggs in oil may double or even triple the fat and cholesterol content of an egg dish.
According to the United States Department of Agriculture, a raw yolk from one standard, large egg provides the followingTrusted Source:
- 55 calories
- 2.70 g of protein
- 4.51 g of fat
- 184 milligrams (mg) of cholesterol
- 0.61 g of carbohydrate
- 0.10 g of sugar
- 0 g of dietary fiber
Egg yolks contain at least seven essential minerals, including:
Egg yolks are a plentiful source of many vitamins, especially fat- and water-soluble vitamins.
The table below outlines the vitamin content of one large (17 g) egg yolk.
| Thiamin | 0.030 mg |
| Riboflavin | 0.090 mg |
| Niacin | 0.004 mg |
| Vitamin B-6 | 0.060 mg |
| Vitamin B-12 | 0.332 micrograms (mcg) |
| Vitamin A | 64.8 mcg |
| Vitamin E | 0.439 mg |
| Vitamin D (D-2 and D-3) | 0.918 mcg |
| Vitamin K | 0.119 mcg |
Duck, quail, goose, and turkey eggs contain higher amountsTrusted Source of many vital nutrients than chicken eggs.
Yolk vs. egg white
In comparison with the 2.7 g of protein in the yolk of a single, large egg, the white provides 3.6 gTrusted Source.
While the white provides more protein, the yolk contains nearly all of the fat- and water-soluble vitamins and minerals in eggs. Research suggests that consuming whole eggs has more significant benefits than eating egg whites alone.
For example, a 2017 study found that young men who ate whole eggs immediately after performing resistance exercises had higher rates of muscle metabolism than those who consumed only egg whites.
Considerations
The most common health concern relating to eggs is food poisoning from the bacteria Salmonella, which poultry naturally carry. These bacteria may contaminate the eggs.
Salmonella infections can be serious, especially for young children, people with immune conditions, and those over the age of 65 yearsTrusted Source. However, following a few basic safety precautions when purchasing, storing, handling, and cooking eggs significantly reduces the risk of food poisoning.
Tips for safely dealing with eggs include:
- purchasing eggs from a reputable, licensed source or a trusted local farmer
- making sure that eggs do not have cracks or holes in the shell before purchasing them
- storing eggs in the refrigerator at 40°F (4.4°C)
- washing the hands and all exposed surfaces with soap and water immediately after coming into contact with raw eggs
- eating or refrigerating eggs no more than 2 hours after cooking them
- cooking eggs until at least the whites are firm (individuals at higher risk of infection should cook eggs until both the white and yolk are firm)
- cooking egg dishes, such as casseroles or quiches, to an internal temperature of at least 160°F (71.1°C)
- cooking scrambled eggs until firm
- throwing away broken, dirty, or cracked eggs, as well as expired eggs and egg products
- avoiding eggs that have an odd consistency, appearance, or smell
- keeping raw eggs away from other foods, especially foods that do not require cooking
- using pasteurized eggs for dressings and condiments that require soft boiled eggs, such as hollandaise sauce, mayonnaise, and Caesar salad dressing

- +1 931-805-2533
- support@cluckcopoultry.com
- 9338 Hwy 49 E E, Orlinda, TN 37141, United States
Get exciting offers!
Join our email list to get exciting offers from our poultry farm!